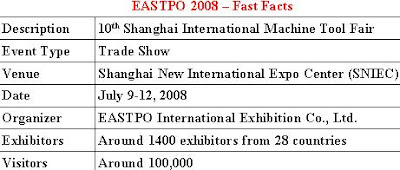
A highly preferred casting method among manufacturers and designers, die casting is an efficient and economical process that offers several advantages for creating parts and components. Because of these advantages, die casting becomes an obvious choice when selecting a manufacturing process for a specific part. However, sometimes the designers must compare the benefits of die casting over other methods, such as plastic injection molding.
A major advantage of die casting over plastic components is that die casting makes stronger parts with closer tolerances, which have higher stability and durability. Die cast components are also known for their superior temperature resistance and electrical properties.
Another thing that is adding value in favor of die castings is that the continuous increase in the prices of oils is having a considerable impact on the price of plastic feed stocks used in manufacturing components. With continuously increasing crude oil prices, the prices of plastic components produced from oil feedstock are bound to increase as well.
Advantages of Die Casting
Although both die casting and plastic injection molding are high-speed manufacturing processes, die casting offers several advantages over plastic components, including-
Strength, weight and heat tolerance – These primary metal characteristics favor die castings over plastic components for a variety of applications. Die cast components are stronger than plastic injection moldings of same dimensions. In addition, the variety of choices available for zinc, aluminum and magnesium alloys allow designers to select materials, which can be used in high temperature conditions.
Dimensional Accuracy & Stability – Die casting process creates parts, which are durable and dimensionally stable, while retaining close tolerances. Plastic components are more susceptible to warping and surface sinking in regions above ribs is far more common. Several die casting alloys also offer better creep resistance.
Multiple Finishing Techniques - Die cast components can be created with smooth & textured surfaces, and can be easily plated or finished with a minimum of surface penetration. Components can be cast with lettering or ornamentation, which allows finer details and higher resistance to wear than plastic parts. In addition, as die casting creates complex shapes within closer tolerances, little or no machining is needed.
Recyclability – According to reports, more than 95% of aluminum die castings manufactured in North America are produced from post consumer recycled aluminum. As the production of recycled aluminum alloy needs less energy than producing the alloy directly from ore or other techniques, there is a significant conservation of non-renewable energy resources. More than 85% of aluminum in a car is presently reclaimed and recycled, while most of the plastic in a scrapped vehicle is considered as a fluff and is sent to waste dumps.